- Services
- Industries
- Automotive
- Battery
- Building inspection
- Fire alarms system testing
- Household appliances
- Installation materials
- Industrial machinery
- IT & audio video
- Laboratory, test & measurement
- Lighting equipment
- Maritime, oil & gas
- Medical & healthcare equipment
- Military & aerospace product testing
- Wireless & telecom
- Resources
- About
- Blog
- Events
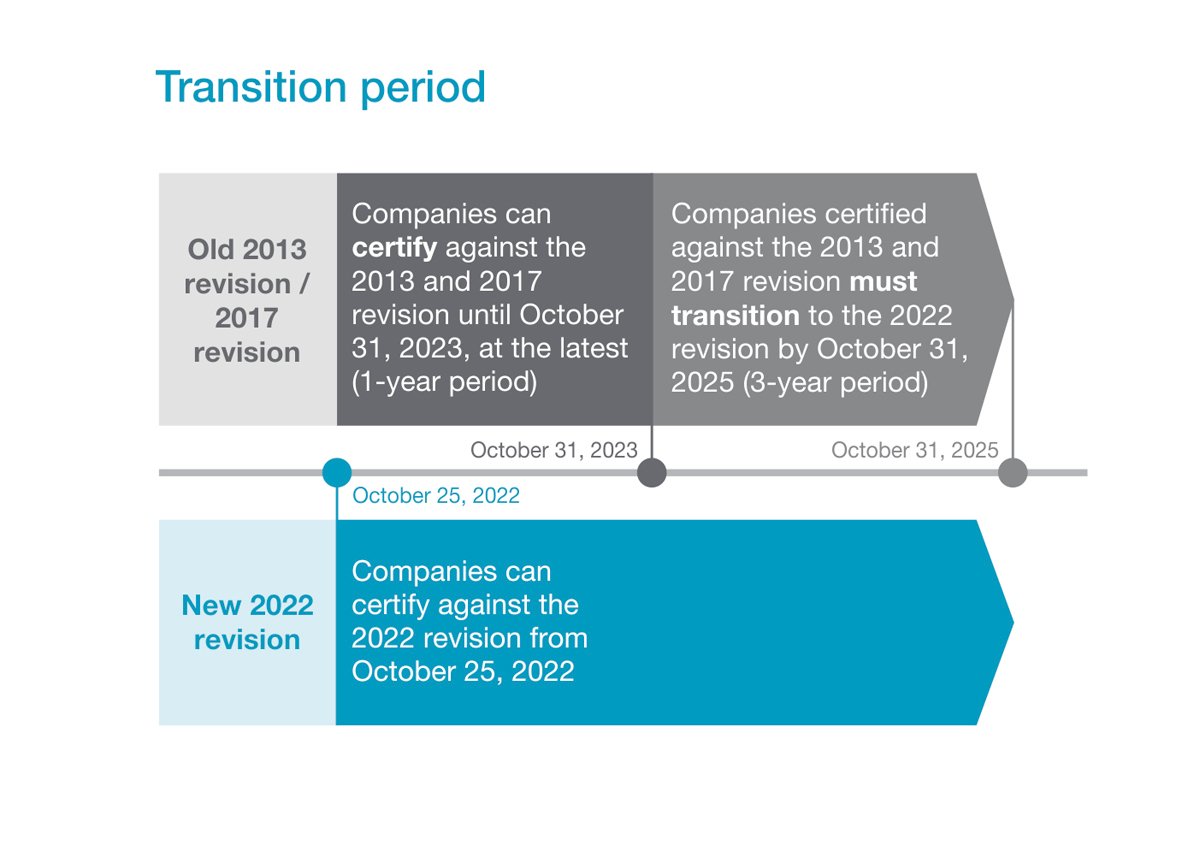
On 25 October 2022, the ISO/IEC 27001:2022 was released and brings some changes compared to the old version. All certificates issued to the previous version of the information security management system standard (ISO/IEC 27001:2013) will have an expiration date of 31 October 2025.
 Why information security is important for the business?
Why information security is important for the business?
In today’s volatile business environment, information security, cybersecurity and privacy protection are vital for companies. Organizations of all sizes and in all sectors must make sure they manage the security of their assets, e.g., financial information, intellectual property, employee data, and third-party information. ISO/IEC 27001:2022 is the information security standard that specify which requirements are necessary for implementing security controls within an organization.
What are the changes to the new ISO/IEC 27001:2022 standard?
There are three change areas in the new information security standard which we think are most important to highlight. These include new title, changes in Annex A and changes to clauses 4-10. To give you an overview, we have elaborated on the changes below.
1. New title
The title of the standard has been updated and it is now called: ISO/IEC 27001:2022 Information Security, Cybersecurity and Privacy Protection.
2. Annex A changes
Annex A has changed its title to Information security controls reference (from previous ‘Reference control objectives and controls’). As the title change indicates, the control group’s reference objectives have been removed in the ISO/IEC 27001:2022.
Furthermore, the number of controls has been updated. Below, we have listed the 11 new controls which have been added to Annex A:
- Threat intelligence
- Information security for the use of cloud services
- ICT readiness for business continuity
- Physical security monitoring
- Configuration management
- Information deletion
- Data masking
- Data leakage prevention
- Monitoring activities
- Web filtering
- Secure coding
Furthermore, the control groups in ISO/IEC 27001:2022 have been divided into 4 sections (instead of 14 in the previous version). These four sections are listed below:
- A.5 Organizational controls (37 controls)
- A.6 People controls (8 controls)
- A.7 Physical controls (14 controls)
- A.8 Technological controls (34 controls)
These four sections consist of 93 controls, which is a decrease from the previous’ standards 114. The decrease is a result from merging some of the controls.
 3. Changes to chapter 4-10
3. Changes to chapter 4-10
Several minor changes had been made to clauses 4-10. The most prominent changes have taken place to clauses 4.2, 6.3, and 8.1.
4.2. Understanding the needs and expectations of interested parties
Added item (c) for requirements from interested parties
6.3 Added subchapter: Planning of changes
When the organization determines the need for changes to the information security management system, the changes shall be carried out in a planned manner.
8.1 Operational planning and control
Changes to:
The organization shall plan, implement and control the processes needed to meet requirements, and to implement the actions determined in Clause 6, by:
- establishing criteria for the processes.
- implementing control of the processes in accordance with the criteria.
Documented information shall be available to the extent necessary to have confidence that the processes have been carried out as planned.
How can Nemko help?

